UNVEILING THE WONDERS OF CT SCANS: FROM INCEPTION TO INTERPRETATION
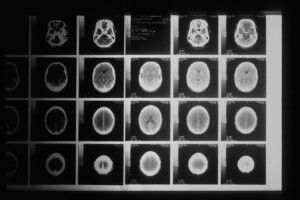
Computed Tomography (CT) scans have revolutionized medical imaging, enabling detailed cross-sectional views of the human body. In this post, we’ll delve into the fascinating journey of CT technology, how it works, and the process of reading and producing reports from CT scans.
The Birth of CT Scans
CT scans were first developed by British engineer Sir Godfrey Hounsfield and South African-born physicist Dr. Allan Cormack in the early 1970s. Their pioneering work led to the invention of the first clinical CT scanner, which produced cross-sectional images of the body using X-ray technology.
CT Scanning Process
- X–ray Generation: CT scanners incorporate X-ray tubes that emit a controlled beam of X-rays. The beam passes through the body and interacts differently with various tissues, resulting in varying levels of X-ray absorption.
- Detectors and Data Acquisition: Opposite the X-ray source, an array of detectors capture the X-rays that pass through the body. These detectors measure the intensity of the X-rays, forming raw data.
- Rotational Scanning: The X-ray source and detector array rotate around the patient, capturing multiple views from different angles.
- Image Reconstruction: Specialized computer algorithms process the raw data to create detailed cross-sectional images, or “slices,” of the body. These images represent different tissue densities, providing valuable anatomical information.
Reading and Interpreting CT Scan Reports
Interpreting CT scan reports requires expertise from radiologists who specialize in analyzing medical images. The process involves the following steps:
1. Image Review: Radiologists examine the CT images slice by slice, systematically evaluating the different anatomical structures, organs, and areas of interest.
2. Identification of Abnormalities: Radiologists identify any anomalies, such as tumors, fractures, infections, or other pathologies, by comparing the observed structures with the expected normal appearance.
3. Analysis and Diagnosis: Radiologists analyze the findings within the clinical context, taking into account patient history and symptoms. They provide a detailed interpretation of the scan, including the location, size, and characteristics of any abnormalities.
4. Report Generation: Radiologists compile their findings into a formal written report, which includes a description of the scan, key observations, and a diagnostic impression. This report is then shared with the referring healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment planning.
Producing CT Scan Results
The CT scan images, along with the radiologist’s report, form the final results. These results aid healthcare providers in making accurate diagnoses, designing treatment plans, monitoring progress, and guiding interventions.
CT scans have transformed medical diagnostics, providing detailed and precise images of the human body. From their inception as an innovative imaging technology to the interpretation and generation of results, CT scans have become an indispensable tool in healthcare. The continuous advancements in CT technology and radiology practices ensure enhanced accuracy, safety, and patient care, enabling improved medical decision-making and ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes.
Take the first step toward providing your loved one with the exceptional care they deserve. Contact us today at (281)892-1400 to schedule a personalized tour and learn more about our memory care and assisted living services. Our friendly team is ready to answer your questions and guide you through the process of finding the perfect caregiver at Kingwood Memory Care & Assisted Living. Together, we can create a supportive and nurturing environment where individuals with memory issues can thrive and lead fulfilling lives.
